Risk Assessment
The following flowchart shows the risk assessment process defined by ISO 12100.
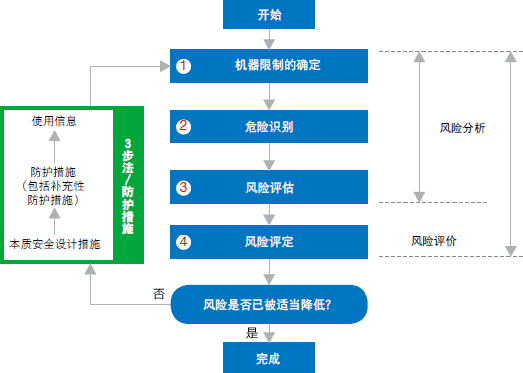
1. Determination of Mechanical Limits
Risk assessment begins with the determination of mechanical limits and also considers the various stages of mechanical life. This means that in an integrated process, the characteristics and performance of a machine (or machine family) and the associated people, environment and product should be determined by mechanical constraints.
2. Hazard identification
Once machinery limits have been established, a key step in machinery risk assessment is the systematic identification of reasonably foreseeable hazards (both permanent and accidental), hazardous situations and/or hazardous events at all stages of the machine's life cycle.
3. Risk assessment
After hazard identification has been completed, a risk assessment must be carried out for each hazard situation by identifying risk elements. Issues such as personnel, duration of exposure, suitability of protective measures, etc. must be considered when determining these risk elements.
4. Risk assessment
After a risk assessment is completed, a risk assessment must be carried out if risk reduction is required. If risk reduction is required, appropriate safeguards must be selected and implemented.
What are usage restrictions?
Limitations of use include intended application and reasonably foreseeable misuse.
What are space constraints?
Space constraints include range of motion or human-machine interaction (eg, operator-machine interface).
What is the time limit?
Time limits include the life limit of the machinery and/or some of its parts.
What is Hazard Identification?
It refers to the identification of potential sources of hazard. Hazards may persist during the intended use of the machine or they may arise unexpectedly.
Hazard identification
mechanical hazard
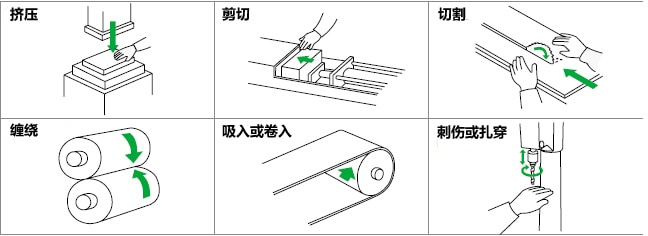
other dangers
Electrical hazards, thermal hazards, hazards due to noise, hazards due to vibration, hazards due to radiation, hazards due to materials and substances, hazards due to neglect of ergonomic principles, etc.
Evaluate
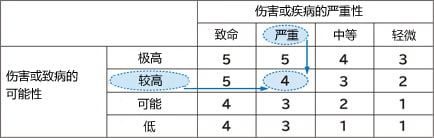
Example 1: Using a matrix
Example of judgment with severity value "(2) critical" and likelihood value "(2) high"
What is a risk assessment?
Identify the severity of possible hazards and the probability of such hazards occurring.
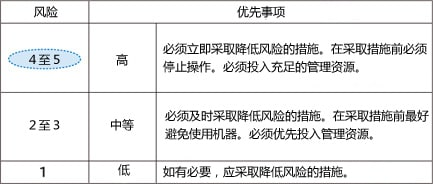
What is risk assessment?
Based on the risk analysis, it is judged whether the risk reduction target has been achieved.




